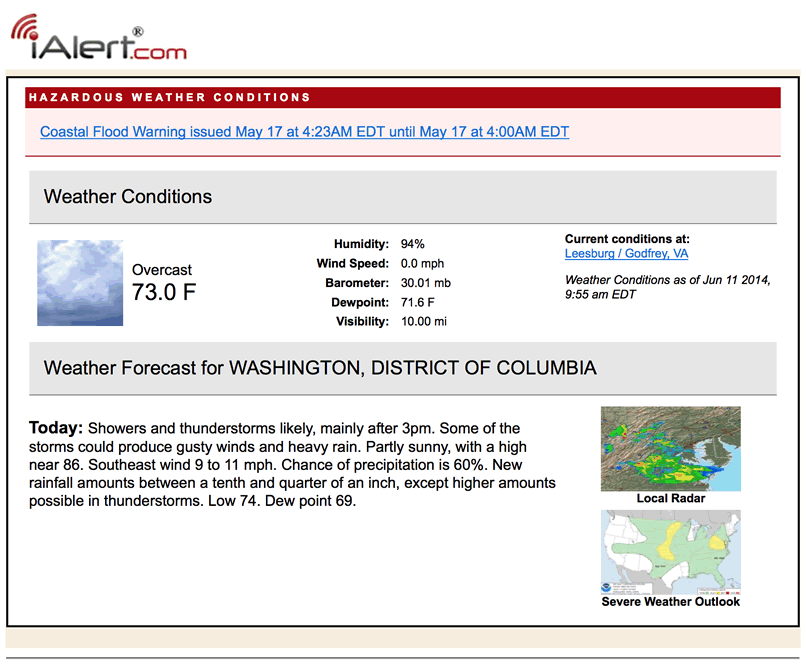
Be prepared with the most accurate 10-day forecast for Post, TX with highs, lows, chance of precipitation from The Weather Channel and Weather.com Post, TX Weather Forecast, with current conditions, wind, air quality, and what to expect for the next 3 days.
Post Weather Forecasts. Weather Underground provides local & long-range weather forecasts, weatherreports, maps & tropical weather conditions for the Post area. Hourly weather forecast in Post, TX. Check current conditions in Post, TX with radar, hourly, and more.
Related Posts of Post/weather :
Be prepared with the most accurate 10-day forecast for Post, TX with highs, lows,
Post, TX Weather Forecast, with current conditions, wind, air quality, and what to expect for the next 3 days.
Post Weather Forecasts. Weather Underground provides local & long-range
Hourly weather forecast in Post, TX. Check current conditions in Post, TX with radar, hourly, and more.
Post weather tomorrow and 5 day forecast with this week's outlook providing day and
Weathered Post Prints for sale
Weather for Postville Newfoundland and Labrador Canada
Weather forecast FOX 5 New York
Weather Topped Posts Brookridge Timber Store South West Delivery
Weather forecast Instagram post template Premium Editable Template
Weather forecast Instagram post template Free Photo rawpixel
weathered post by tristiansargeant ePHOTOzine
Weather Forecast for Thursday Dec 21 FOX 11 Los Angeles
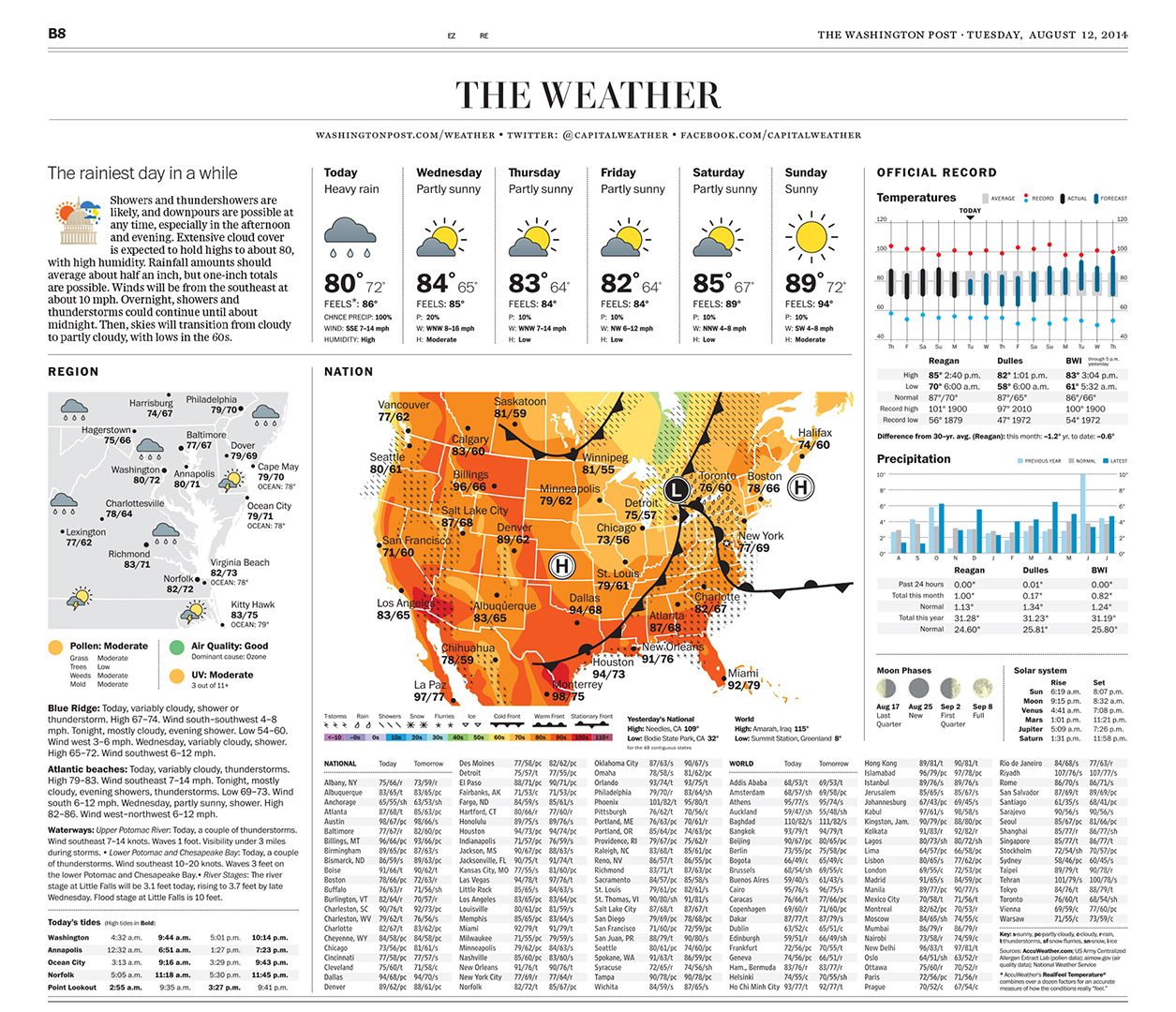
Weather The Washington Post
Weather forecast Newspapers com
Chicago Weather News Accuweather Forecasts abc7chicago com
Post Storm Gretna Nebraska Scott Papek Fine Art Photography
Postal Service Videos at ABC News Video Archive at abcnews com
Chicago Weather News Accuweather Forecasts abc7chicago com
Post Storm Gretna Nebraska Scott Papek Fine Art Photography
Postal Service Videos at ABC News Video Archive at abcnews com
23 166 Weathering posts Images Stock Photos amp Vectors Shutterstock
Weathered Post Stock Photo Royalty Free FreeImages
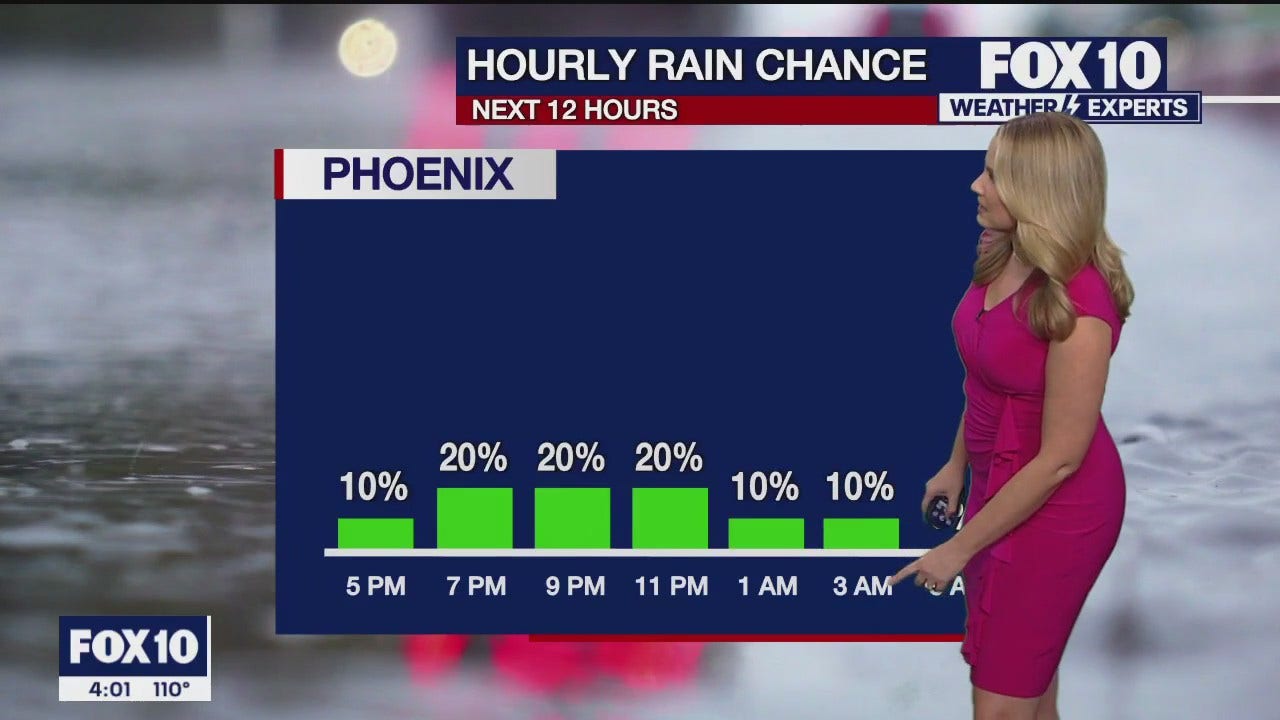
4 p m Weather Forecast 5 3 23 FOX 10 Phoenix
Weathered post temeplayer Flickr
Weathered post on beach Stock Photo Alamy
post rain mike wentworth Flickr
Weathered post Michael Bell Flickr
4 p m Weather Forecast 9 12 23 FOX 10 Phoenix
Post HD Png Download Transparent Png Image PNGitem
Dramatic Post Storm Photos
4 p m Weather Forecast 1 2 23 FOX 10 Phoenix
Weathered Wooden Post Stock Photo Alamy
Weather Forecast 10 31 23 FOX 10 Phoenix
10 p m Weather Forecast 2 12 23 FOX 10 Phoenix
Weather Forecast FOX 5 New York
Monday Afternoon Forecast
Weathered Post Paul Schadler Flickr
Weathered Post uploaded for the Amazing Amateur group Terri Flickr
Weathered Posts by GedG Pentax User
Weathered Post Architecture Photos Monochrome Capture
Weather forecast Keeping it mild through the weekend in PDX
Post Free Photo Download FreeImages
Chicago Weather Freezing rain advisory issued ABC7 Chicago
Chicago Weather Freezing rain advisory issued ABC7 Chicago
Share weather postcards or send a weather report with the ABC7 Weather
The Weather Channel Android Apps on Google Play
Postcard Picture Weather continues today firstcoastnews com
Philadelphia weather forecast AccuWeather forecast for Pennsylvania
Chicago AccuWeather Warm with strong storms Wednesday ABC7 Chicago
Post What It Is and How to Join It
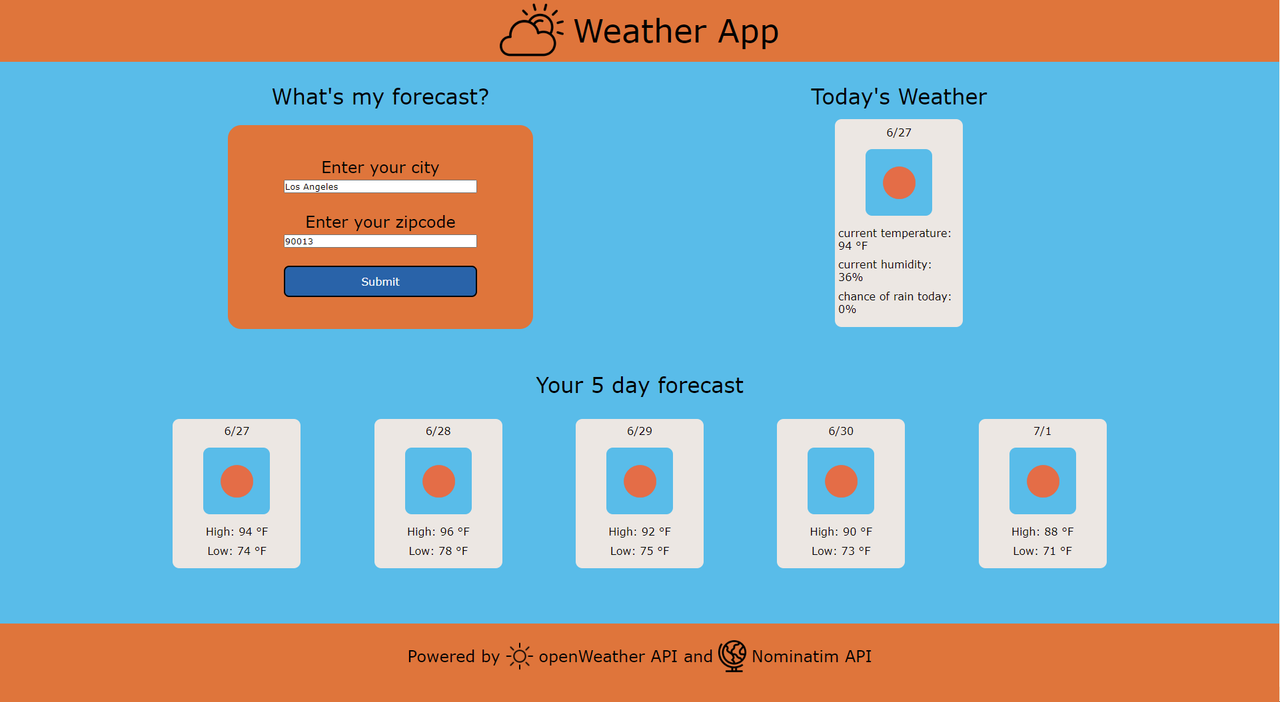
Sample Daily Weather Forecasts by Email and Text Message Weather and
4 p m Weather Forecast 8 8 23 FOX 10 Phoenix
4 p m Weather Forecast 8 23 23 FOX 10 Phoenix
Weather Post Island Health
4 p m Weather Forecast 5 10 23 FOX 10 Phoenix
PM Update Our weather stays fantastic through Friday The Washington Post
Chicago Weather Mostly clear quiet ABC7 Chicago
PM Update Saturday afternoon forecast takes a rainy turn The
Postponed Due to Weather Useful Tips for Urgent Event Communication
Postal Carriers Feeling Brunt Of Weather News Sports Jobs Post
Here s what to expect from Thursday s weather forecast
What To Expect From Post s POST Q3 Earnings The Globe and Mail
Five signs your tax preparer may be a fraud The Washington Post
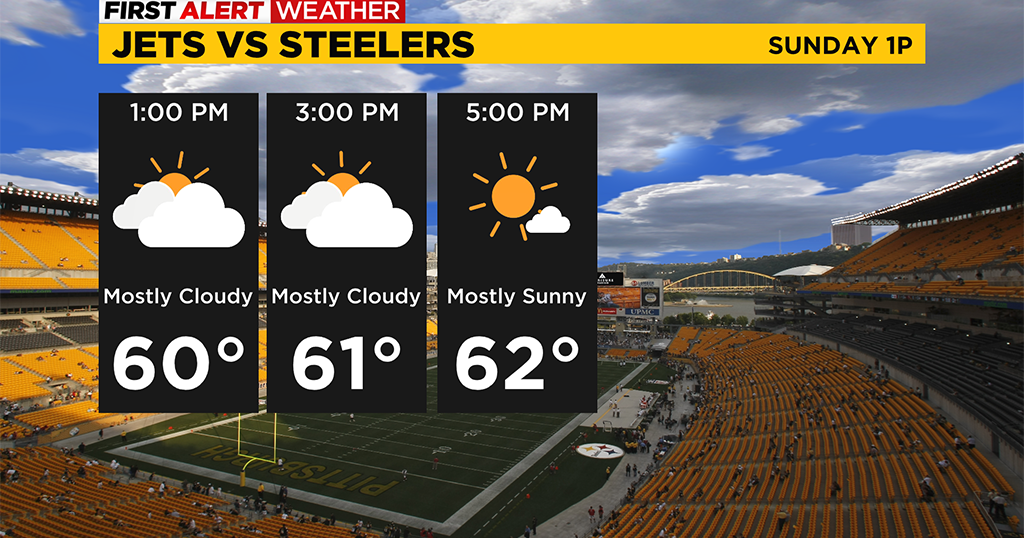
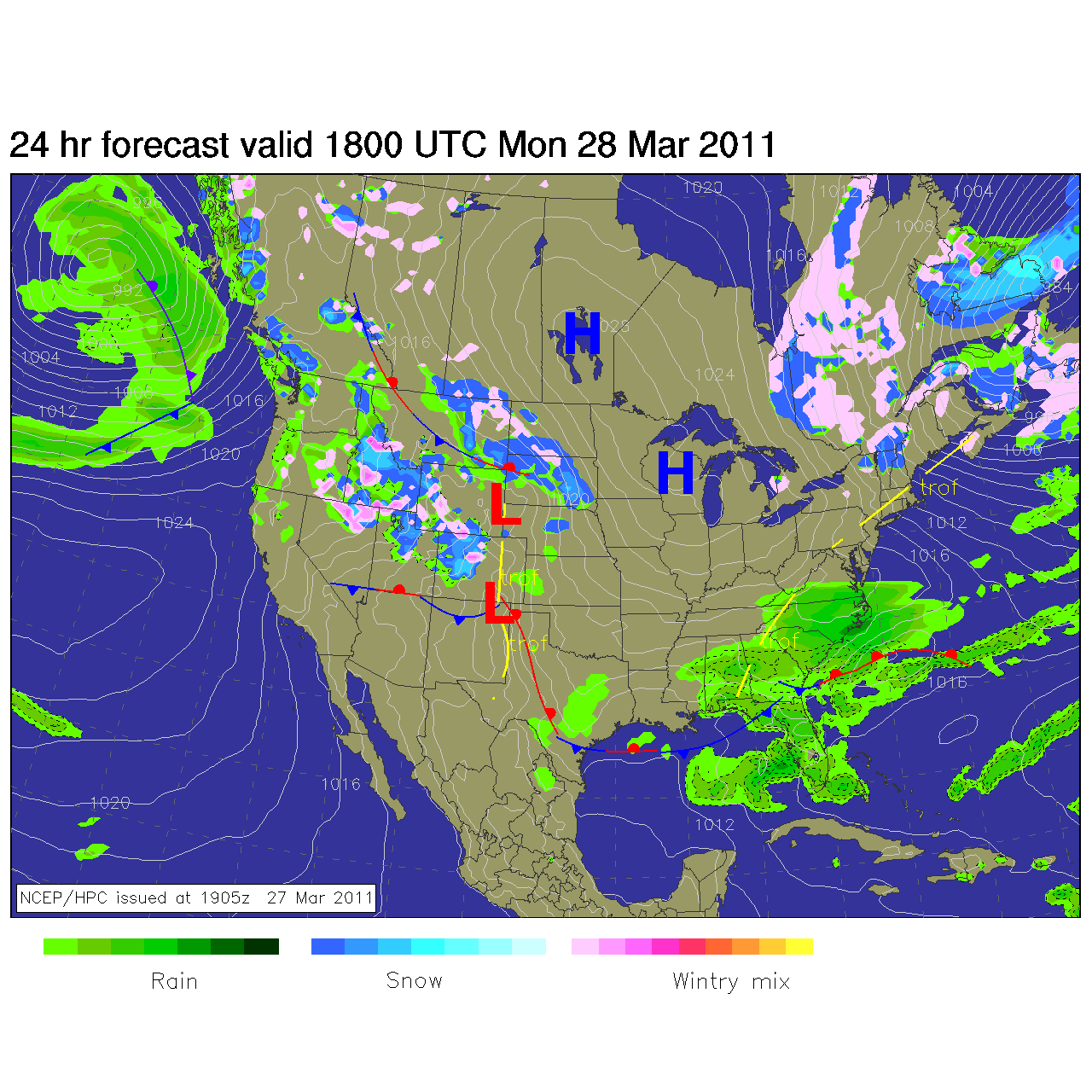
Pittsburgh Weather Post Tropical Ian moves out of the area throughout
69News Weather Forecast Video 01 09 2024 Forecast Video wfmz com
69News Weather Forecast Video 02 28 2024 Forecast Video wfmz com
Customers rush to the post office before winter storms kare11 com
Weather Post and Clouds Photograph by Bill Driscoll Fine Art America
69News Weather Forecast Video 01 12 2024 Forecast Video wfmz com
8 Examples of Weather Related Posts Bound to Produce More Engagement
Post/weather - The pictures related to be able to Post/weather in the following paragraphs, hopefully they will can be useful and will increase your knowledge. Appreciate you for making the effort to be able to visit our website and even read our articles. Cya ~.


















































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/post-news-817a2fe415ed44db8583e87ceb7c49e7.jpg)